Capsule Endoscopy
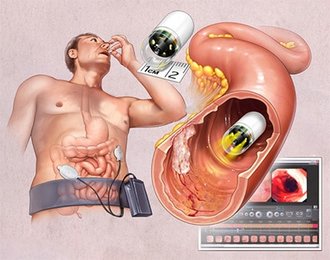
Video capsule endoscopy is a procedure where a patient swallows a wireless camera about the size of a large pill. The camera then takes thousands of still pictures while it travels through the digestive tract. These pictures are then assembled into a video that your gastroenterologist can watch later.
What are the indications for a small bowel capsule endoscopy?
The most common and best indications for small bowel capsule endoscopy are the following:
It can also be used to diagnose small bowel polyps and cancer as well as celiac disease.
- occult gastrointestinal bleeding after a negative gastroscopy and colonoscopy
- suspicion of Crohn's disease involving the small bowel
It can also be used to diagnose small bowel polyps and cancer as well as celiac disease.
Are there any risks involved?
In general it is very safe. The main risk is that the capsule may not pass and remain retained in the small bowel. This can occur in patients who have strictures or fistulas of the small intestine of who have had surgery of the small intestine.
One option to verify if a capsule can pass is to perform a patency capsule test. A patient swallows a capsule the exact shape and size of the the regular capsule but that will begin to dissolve 30 hours later. The patient needs to take an x-ray the following day to see if the capsule is still retained in the small bowel. If not, the risk of capsule retention is felt to be reasonable enough to proceed with the real capsule endoscopy.
Patients who have implantable defibrillators or pacemakers are not recommended to have the test.
One option to verify if a capsule can pass is to perform a patency capsule test. A patient swallows a capsule the exact shape and size of the the regular capsule but that will begin to dissolve 30 hours later. The patient needs to take an x-ray the following day to see if the capsule is still retained in the small bowel. If not, the risk of capsule retention is felt to be reasonable enough to proceed with the real capsule endoscopy.
Patients who have implantable defibrillators or pacemakers are not recommended to have the test.
What can I expect the day of the exam?
The nurse will discuss the procedure with you and have you sign a consent form. The nurse will show you how to wear the recorder on a special belt around your waist. The camera sends images to the recorder that stores the images.
Once the recorder is connected and ready, you swallow the camera capsule with water.
You can then go about your day as you usually would. You should avoid strenuous activity, such as running and jumping.
You will need to wait two hours after you swallow the capsule to resume drinking clear liquids. After four hours, you can have a light lunch or a snack.
The capsule endoscopy procedure is complete after eight hours or when you see the camera capsule in the toilet after a bowel movement, whichever comes first. Remove the recorder from your body, pack them in a bag and follow the instructions for returning the equipment. You can flush the camera capsule down the toilet.
If you don't see the capsule in the toilet within two weeks, contact your doctor. Your doctor might order an X-ray to see if the capsule is still in your body.
Once the recorder is connected and ready, you swallow the camera capsule with water.
You can then go about your day as you usually would. You should avoid strenuous activity, such as running and jumping.
You will need to wait two hours after you swallow the capsule to resume drinking clear liquids. After four hours, you can have a light lunch or a snack.
The capsule endoscopy procedure is complete after eight hours or when you see the camera capsule in the toilet after a bowel movement, whichever comes first. Remove the recorder from your body, pack them in a bag and follow the instructions for returning the equipment. You can flush the camera capsule down the toilet.
If you don't see the capsule in the toilet within two weeks, contact your doctor. Your doctor might order an X-ray to see if the capsule is still in your body.
|
Click on the button for the preparation form
|
|
www.ourdigestivehealth.com
www.GadFriedman.com |